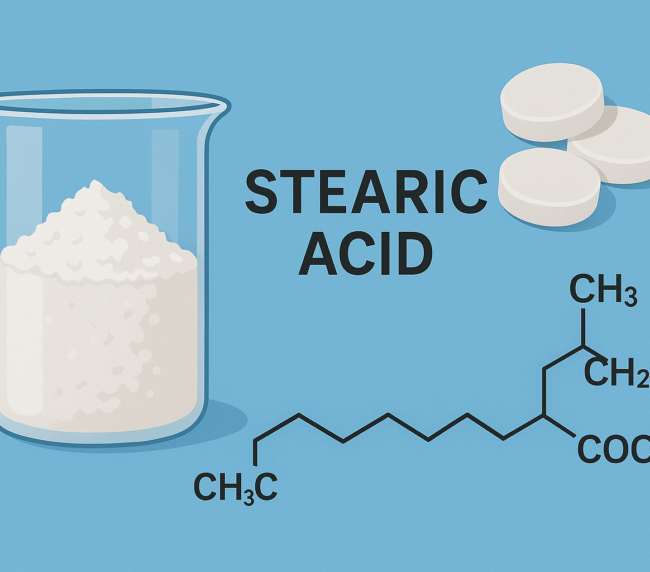
Calcium stearate is a fine, white to yellowish-white, bulky powder with a slight fatty odor. It is insoluble in water, has a soft texture, and melts at around 149–160 °C. Commonly used as a lubricant, it is composed mainly of calcium salts of stearic and palmitic acids.
Chemical Name and CAS Registry Number :-Octadecanoic acid calcium salt [1592-23-0]
Functional Category :-Tablet and capsule lubricant